Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is an enzyme that plays a significant role in cancer by helping tumors evade the immune system. IDO catalyzes the first step in degrading the essential amino acid tryptophan into kynurenine. This process depletes tryptophan in the tumor microenvironment and accumulates immunosuppressive metabolites. This article examines the significance of IDO as a biomarker in cancer, its potential in diagnosis and prognosis, and its implications for therapeutic strategies. One notable supplier in this field is Gentaur. They specialize in providing a wide range of molecular products
IDO Pathway and Its Role in Tumor Immunology
Mechanism of IDO-Mediated Immunosuppression
IDO1, the most studied isoform of the IDO family, is expressed in various cell types, including dendritic cells, macrophages, and tumor cells. When induced by pro-inflammatory signals like interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), IDO1 activity leads to tryptophan depletion in the tumor microenvironment. The resulting lack of tryptophan inhibits the proliferation of effector T cells and induces anergy. Additionally, kynurenine and other metabolites can activate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) pathway, promoting the differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells into regulatory T cells (Tregs) and enhancing their suppressive functions.
IDO in the Tumor Microenvironment
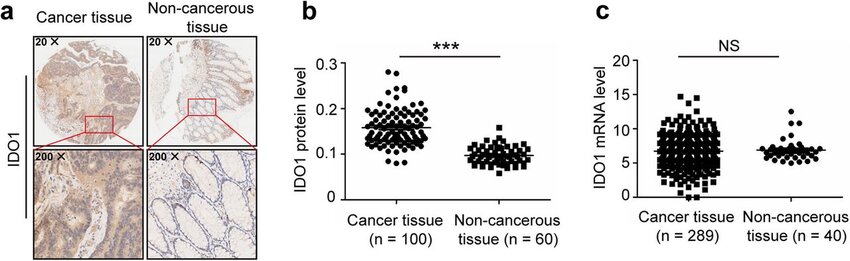
IDO1 expression has been observed in both tumor cells and infiltrating immune cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME). The expression of IDO1 correlates with poor prognosis in several cancer types, including melanoma, ovarian, and colorectal cancers, highlighting its role in creating an immunosuppressive TME that favors tumor progression.
IDO as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker
Diagnostic Potential
IDO1 expression levels can serve as a diagnostic biomarker to identify tumors with an immunosuppressive phenotype. Techniques such as immunohistochemistry (IHC) and quantitative PCR (qPCR) detect IDO1 expression in tumor tissues. Elevated levels of IDO1 in biopsies may indicate a tumor's ability to evade immune surveillance, providing critical information for the characterization of the tumor immune landscape.
Prognostic Value
Studies have demonstrated the prognostic value of IDO1 expression in various cancers. High IDO1 expression is frequently associated with advanced disease stages, higher tumor grade, and reduced overall survival. For example, in ovarian cancer, patients with high IDO1 expression have significantly shorter progression-free survival compared to those with low expression levels. Such correlations make IDO1 a valuable prognostic marker that can inform treatment decisions and patient management.
Therapeutic Implications and IDO Inhibitors
IDO Inhibition as a Therapeutic Strategy
Targeting the IDO pathway is a promising therapeutic strategy to enhance anti-tumor immunity. IDO inhibitors, such as epacadostat and indoximod, have been developed and tested in clinical trials, often in combination with other immunotherapies like checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies). The rationale is that IDO inhibition can relieve tryptophan-mediated T cell suppression, thereby enhancing the efficacy of checkpoint blockade therapy.
Clinical Trials and Challenges
Early-phase clinical trials have shown that IDO inhibitors can be well-tolerated and exhibit clinical activity in combination therapies. However, recent results from phase III trials, such as the ECHO-301/KEYNOTE-252 trial, have yielded disappointing outcomes, with IDO inhibition failing to improve overall survival when added to pembrolizumab in melanoma patients. These results highlight the complexity of the tumor immune microenvironment and the need for better patient stratification and combination strategies to achieve meaningful clinical benefits.
Conclusion
IDO is a critical biomarker in cancer, providing insights into tumor immune evasion mechanisms and offering potential diagnostic and prognostic value. While the therapeutic targeting of IDO has faced challenges, ongoing research and more sophisticated approaches to patient selection and combination therapies hold promise. Understanding and utilizing IDO biomarkers in cancer will continue to be a pivotal area of investigation to improve cancer immunotherapy outcomes.