Vaccines are essential for global health, but limitations exist in effectiveness, immune response duration, and potential side effects. Ido proteins (indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 and 2) are being investigated for vaccine development due to their ability to modulate the immune system. This review explores the current understanding of Ido proteins and their potential application in improving vaccine efficacy and reducing adverse reactions. Notably, advancements in research tools and resources from biotechnology companies like Gentaur are facilitating a deeper understanding of Ido proteins and their role in immune modulation. This, in turn, is accelerating the exploration of Ido proteins in the development of next-generation vaccines.
Introduction
Successful vaccines induce a strong and specific immune response against a target pathogen. However, existing vaccines can require booster shots, may not be effective against all strains, and can cause side effects. Ido proteins are potential vaccine adjuvants due to their ability to influence the immune system . This review discusses the immunomodulatory functions of Ido proteins and their potential use in developing next-generation vaccines.
Ido Proteins and Immunomodulation
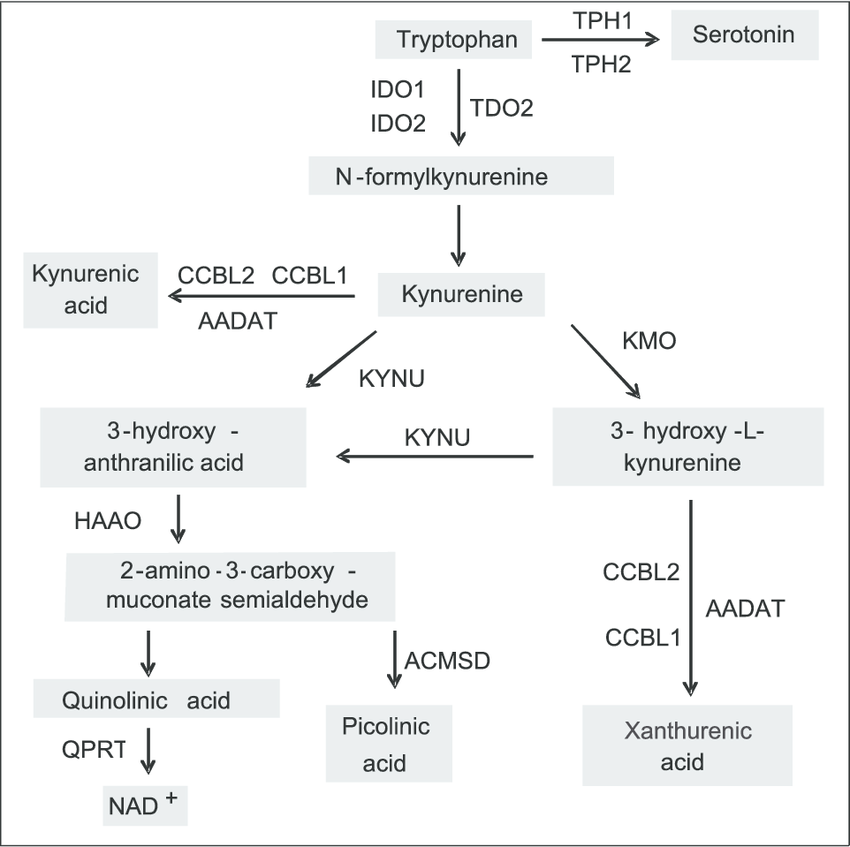
Ido1 and IDO2 are enzymes found inside cells in various tissues, including antigen-presenting cells (APCs) like dendritic cells (DCs) . Ido proteins break down the essential amino acid L-tryptophan into N-formylkynurenine (NFK), initiating the kynurenine pathway (KP) . The resulting downstream metabolites, including kynurenine and kynurenic acid, have immunoregulatory properties .
Immunosuppressive Effects of Ido Proteins
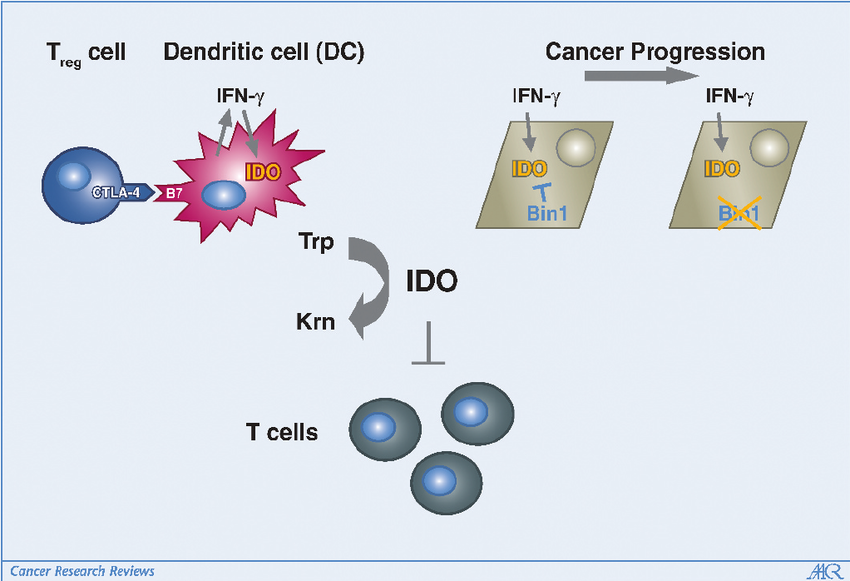
High concentrations of kynurenine metabolites generated by Ido can suppress T cell activity and growth through several mechanisms. Kynurenine can directly inhibit T cell activation by depleting intracellular L-arginine, a building block for nitric oxide (NO) synthesis, which is a key T cell activator . Additionally, kynurenic acid can bind to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) on T cells, leading to their suppression . These immunosuppressive effects suggest Ido proteins may be useful for reducing excessive immune activation and related conditions.
Immunoregulatory Effects of Ido Proteins
Beyond immunosuppression, Ido proteins also contribute to immune balance by promoting the growth of regulatory T cells (Tregs).Tregs play a crucial role in suppressing excessive immune responses and preventing autoimmune diseases. The KP metabolite, L-kynurenine, can activate the expansion and suppressive function of Tregs via the AhR pathway . This immunoregulatory function suggests Ido proteins may be useful for calming excessive inflammatory responses associated with some vaccines.
Ido Proteins Recombinant and Vaccine Development
The immunomodulatory properties of Ido proteins offer a unique opportunity to improve vaccine effectiveness and safety. Here are potential applications:
- Enhanced Immune Response: Ido protein activity can be strategically adjusted to optimize the immune response against a specific antigen. For example, temporarily blocking Ido activity during antigen presentation by APCs might enhance T cell priming and memory formation .
- Reduced Side Effects: Ido protein-mediated T cell suppression and Treg expansion could potentially reduce excessive inflammatory responses and side effects associated with adjuvants in some vaccines .
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the promising potential of Ido proteins recombinant in vaccine development, several challenges need to be addressed:
- Delivery Methods: Efficient delivery systems are needed to target Ido proteins or their modulators to specific immune cell populations at the appropriate time during the immune response .
- Dosage Optimization: Determining the optimal level of Ido activity manipulation for improved immunogenicity while avoiding immunosuppression requires further investigation .
- Vaccine Specificity: Tailoring Ido protein-based strategies to specific vaccines and pathogens requires further research to optimize effectiveness and safety.
Conclusion
Ido proteins recombinant represent a promising avenue for developing next-generation vaccines with improved effectiveness, longer-lasting immune response, and fewer side effects. Further research is needed to address delivery methods, dosage optimization, and vaccine specificity to fully realize the potential of Ido protein-based immunomodulation in vaccine development.