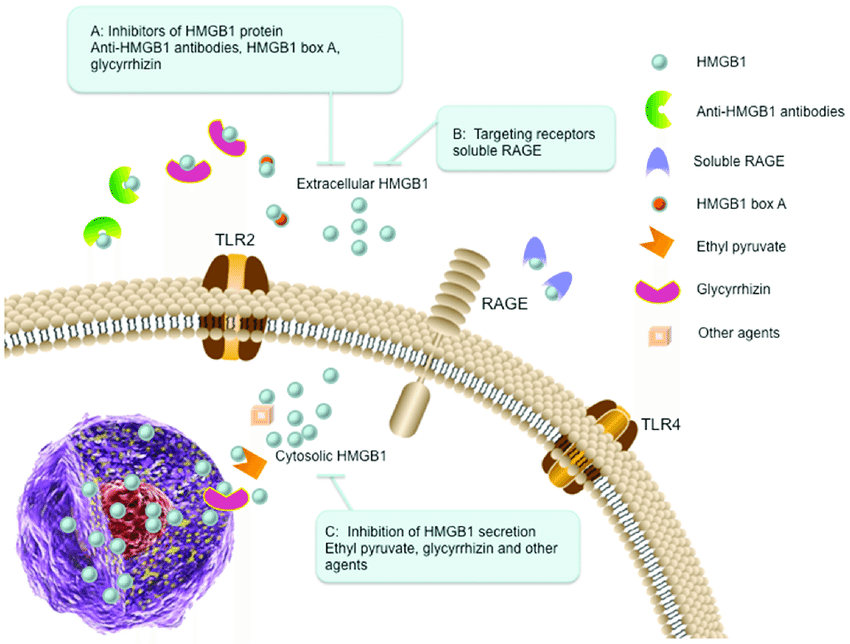
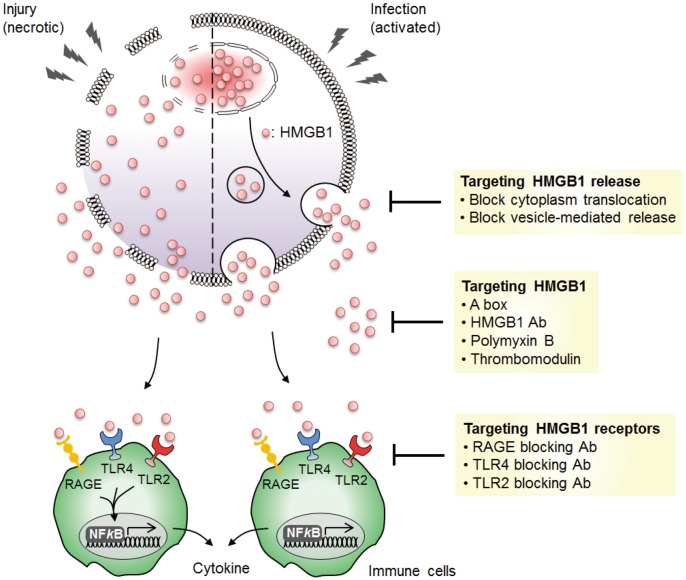
High-mobility group box protein 1 (HMG-B1) is a protein present throughout the cell nucleus and plays various roles, including DNA repair, chromatin organization, and regulating gene activity. Recent research suggests HMG-B1 involvement in various diseases when its expression levels deviate from normal. Western blotting, a key technique for protein analysis, is valuable for investigating HMG-B1 expression in specific disease contexts.
suppliers like GENTAUR offer a variety of resources specifically suited for HMG-B1 research using Western blotting. These resources may include validated antibodies, buffers, and other essential reagents, allowing researchers to perform reliable and reproducible experiments investigating HMG-B1 expression in various disease models.
HMG-B1 and Disease Associations
- Cancer: Studies have shown increased HMG-B1 levels in some cancers, including breast, lung, and colon cancers. Western blotting allows researchers to directly measure HMG-B1 levels in tumor tissues compared to healthy controls, potentially providing insights into its role in cancer development.
- Inflammatory Diseases: When cells are stressed or injured, HMG-B1 can be released outside the cell and act as a signal molecule. Western blotting can detect and measure HMG-B1 levels in biological fluids like blood serum or plasma, aiding research into its involvement in inflammatory diseases like sepsis or rheumatoid arthritis.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Emerging evidence suggests a possible link between abnormal HMG-B1 levels and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Western blotting can be used to analyze HMG-B1 expression in brain tissues from patients and animal models, helping to understand its contribution to these pathologies.
Western Blotting Strategies for HMG-B1 Analysis:
- Cell Lysates vs. Tissue Homogenates: Depending on the research question, Western blotting can be performed on extracts made from cells (for studies in cell culture) or on homogenates made from tissues (for analyzing HMG-B1 expression in specific organs).
- Antibody Selection: Using a specific and sensitive antibody that targets HMG-B1 is crucial. Commercially available antibodies validated for Western blotting by reputable companies are recommended.
- Loading Controls: Including proteins whose levels remain relatively constant across samples (housekeeping genes like β-actin or GAPDH) helps ensure accurate measurement of HMG-B1 expression between samples.
- Quantification Techniques: Software can be used to analyze the intensity of HMG-B1 bands on Western blots, allowing for comparisons between groups. Normalization to loading controls is essential for accurate quantification.
Future Directions:
Western blotting remains a powerful tool for investigating HMG-B1 expression in various disease contexts. Advancements in antibody development and protein quantification methods hold promise for further refining the analysis of HMG-B1 and its role in diverse pathologies.